Mechanical Behavior of Buried Steel Pipelines under Ground-Induced Actions
(completed, October 2013)
Period:
2007 - present (in progress)
Summary:
The research investigates the mechanical behaviour of buried steel pipelines subjected to ground-induced actions, such as crossing an active tectonic fault, liquefaction & lateral spreading, or differential settlements. The soil-pipeline system is modelled rigorously through finite elements, which account for large strains and displacements, nonlinear material behaviour and special conditions of contact and friction on the soil-pipe interface. Considering steel pipelines of various diameter-to-thickness ratios, and typical steel material for pipeline applications, the research emphasizes on the effects of various soil and pipeline parameters on the structural response of the pipe, with particular emphasis on pipe wall failure due to wrinkling (local buckling) or rupture.
So far, the research has focused on the effects of strike-slip active faults. The effects of shear soil strength, soil stiffness, horizontal fault displacement, width of the fault slip zone, have been investigated. The results are aimed at determining the fault displacement that would cause pipeline failure. The numerical results determine the critical fault displacement versus the pipe diameter-to-thickness ratio, and can be used for pipeline design purposes.
In the course of this research, other ground-induced actions will be considered in the near future, such as normal or reverse faults, liquefaction & lateral spreading, and differential settlements.
Relevant Publications:
In Referred Journals
- Vazouras, P., Karamanos, S. A., and Dakoulas, P., "Finite Element Analysis of Buried Steel Pipelines Under Strike-Slip Fault Displacements", Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, February 2010, submitted for publication.
In Conference Proceedings
- Dakoulas, P., Vazouras, P., and Karamanos, S. A., "Stress State and Limit Strength of Underground Steel Pipelines in Active Faults", 3rd National Conference on Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Seismology, Paper No. 2029, Athens, Greece, November 2008 (in Greek).
- Vazouras, P., Dakoulas, P., and Karamanos, S. A., "Finite Element Analysis of Buried Pipelines Under Seismic-Fault Displacement", COMPDYN2009Conference, paper CD441, Rhodos, Greece, June 2009.
Figures:
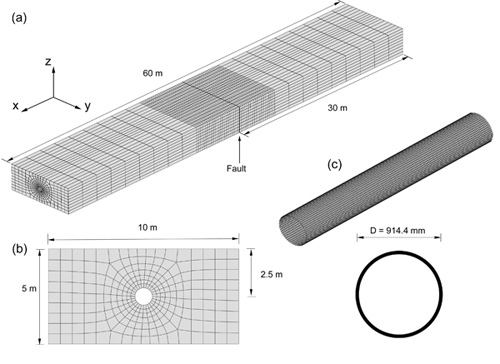
Figure 1: Finite element model of the (a) soil formation with tectonic fault, (b) soil cross-section and (c) steel pipeline.
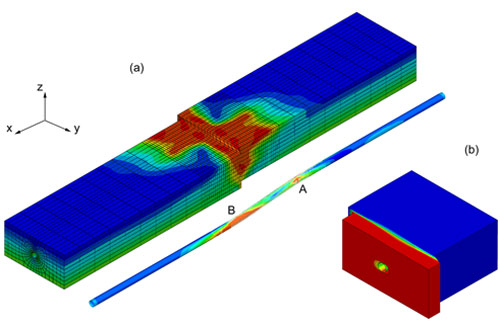
Figure 2: (a) Deformation of the pipeline-soil system after fault displacement; finite element results depict the von Mises stress. (b) Detail of fault displacement Ut, illustrating the development of a gap opening at the soil - pipe interface.
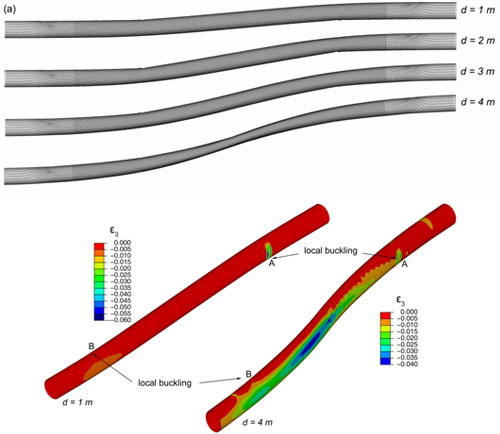
Figure 3: (a) Plan view of deformed shape of a pipeline for d = 1, 2, 3, and 4 m (b) Distribution of minor principal strain E1 for seismic fault displacement equal to 1 m and 4 m. (X65 pipe, D/t=72, Clay I,W= 0.33 m, P= 0).